Difference between revisions of "TELEMAC"
m (→Quick summary) |
m (→Quick summary) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Developed by: Laboratoire National d'Hydraulique et Environnement (LNHE), part of the R&D group of Électricité de France. | Developed by: Laboratoire National d'Hydraulique et Environnement (LNHE), part of the R&D group of Électricité de France. | ||
| + | |||
Date: 1991 (and later) | Date: 1991 (and later) | ||
| + | |||
Type: [[:Category:Tools|Tool]] | Type: [[:Category:Tools|Tool]] | ||
Revision as of 13:54, 30 September 2020
Contents
Quick summary
TELEMAC is a 2d shallow water and 3D RANS Navier-Stokes code for hydro-morphodynamic computations in mainly rivers. The program is open source.
Developed by: Laboratoire National d'Hydraulique et Environnement (LNHE), part of the R&D group of Électricité de France.
Date: 1991 (and later)
Type: Tool
Introduction
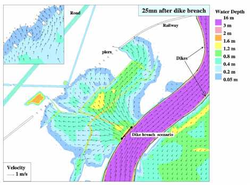
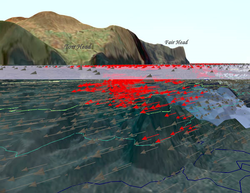
An international consortium of research institutes, agencies and companies manages the open source software TELEMAC (www.opentelemac.org). Originally developed in France, the software is now freely available and the FORTRAN-based source code is open for developers and users. The software is structured in modules, which can be coupled depending on the purpose. The most common module is Telemac-2D, which is a 2D depth averaged, shallow water based hydrodynamic solver for free surface flows. The more complex model,Telemac-3D, provides RANS averaged three dimensional information on the flow. Both modules can be coupled to Sisyphe, the morphological module, representing sediment transport. Figures 1-4 provide an overview of some selected modules. For completeness, the others are Artemis and Tomawac (for wave and coastal areas), Nestor (extension for Sisyphe), and the one-dimensional solver Mascaret.
Application
TELEMAC is well suited to model flow and hydro-morphological processes in rivers, by using either a classical, two-dimensional shallow-water approach or a fully 3D RANS based Navier-Stokes solver. The program has a large number of empirical bed-load and suspended load transport formulae implemented. Additionally, customized developments and extensions can be implemented as described below.
Relevant mitigation measures and test cases
Other information
The availability of the source code makes TELEMAC suitable for developments, extensions and research purposes, beyond the existing framework. On the TELEMAC homepage information on user-specific developments can be found in a source code repository or in the proceedings of the user community events. For example, at TUM the following user-specific extensions have been developed or are currently under development:
- Development for sediment transport to improve the process description and the stability of the code.
- Integration of innovative, data-driven methods instead of classical, morphological simulation approaches.
- Further code optimization for one of the fastest High-Performance-Computer worldwide.
- Concept to provide the computational grid, to estimate relevant parameters and to perform an automated, iterative model calibration.
Relevant literature
- Galland, J.C.; Goutal, N., Hervouet, J.M. (1991), TELEMAC: A New Numerical Model for Solving Shallow Water Equations, Advances in Water Resources, 14 (3): 138-148, https://doi.org/10.1016/0309-1708(91)90006-A
- Goutal, N. and Maurel, F. (2002). A Finite Volume Solver for 1D Shallow-Water Equations Applied to an Actual River.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids; 38:1-19. https://doi.org/10.1002/fld.201
- Goutal, N., Lacombe, J.-M., Zaoui, F., El-Kadi-Abderrezzak, K. (2012). MASCARET: a 1-D Open-Source Software for Flow Hydrodynamic and Water Quality in Open Channel Networks. River Flow 2012 – Murillo (Ed.), pp. 1169-1174