Difference between revisions of "3D sensorless, ultrasound fish tracking"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Quick summary= | =Quick summary= | ||
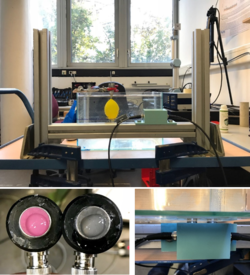
| − | [[file:3d_Sensorless_ultrasound_setup.png|thumb|250px|Figure 1: Experimental setup for testing and development of the 3D sensorless ultrasound fish tracking.]] | + | [[file:3d_Sensorless_ultrasound_setup.png|thumb|250px|Figure 1: Experimental setup for testing and development of the 3D sensorless ultrasound fish tracking (TU Munich.]] |
Developed by: Chair of Hydraulic and Water Resources Engineering, Chair of Non-Destructive Testing, TU Munich | Developed by: Chair of Hydraulic and Water Resources Engineering, Chair of Non-Destructive Testing, TU Munich | ||
Revision as of 17:12, 30 May 2020
Contents
Quick summary
Developed by: Chair of Hydraulic and Water Resources Engineering, Chair of Non-Destructive Testing, TU Munich
Date: February 2019
Introduction
The device (Figure 1) works without tagging fish and is similar to 3D tomographic imaging. It detects fish in rivers with high spatial and temporal resolution over a distance of a couple of hundred meters. Ultra-sonic transducers (receivers and emitters) are positioned in the water. When one transducer emits the others receive the signal. Emitting and receiving cycles around the devices with high frequency. As the resolution is in the range of only a few centimetres it is expected to measure the length of fish and even the species by the shape of the fish bladder.
Application
The device can be used to detect sensorless fish in 3D. This cannot only be used to track fish in 3D but also to adapt operation of a hydropower plant to the needs of migrating fish. During the FIThydro project the TRL level needs to be raised from TRL4 to TRL5. So far, only first results are available and they show good potential. However, there is still a long way to go for a first prototype application in real rivers.
Relevant mitigation measures and test cases
Other information
European patent applied (application 15 188 223.0-1020)
Relevant literature
Contact information
Peter Rutschmann (TUM)