Difference between revisions of "By-passing sediments"
Bendikhansen (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "=Useful MTDs=" to "=Relevant MTDs and test cases=") |
Bendikhansen (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
=Classification Table= | =Classification Table= | ||
{{By-passing sediments}} | {{By-passing sediments}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Relevant Literature= | ||
[[category:Sediment measures]][[category:Measures]] | [[category:Sediment measures]][[category:Measures]] | ||
Revision as of 12:40, 12 March 2020
Contents
Introduction
Dams act as a barrier for sediment transport in river systems. Sediments-laden inflows bring sediments from upstream catchment that will be trapped when reaching the reservoir. Sediments deposit in the bottom of the reservoir and reduce its storage capacity. In geographical areas with very high sediment concentration, reservoirs can be filled after some years, rendering useless the infrastructure. Consequently, sediments are not transported downstream the dam, resulting in sediment starvation in the downstream river. Lack of sediments can induce severe morphological and ecological impacts.
Sediment by-passing is a measure which aims at routing bed-load and part of the suspended sediment load through or around the reservoir (Morris et al. 1998). The objective is to maintain the storage capacity of the reservoir in addition to insure sediment continuity in the river and avoid morphological and ecological impacts (Hauer et al. 2018).
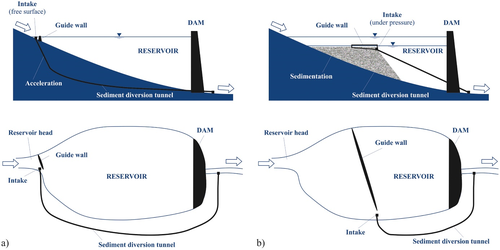
Sediment by-pass consists in diverting bed-load and part of the suspended load around the reservoir to prevent them for entering the reservoir. The sediment-laden inflows are diverted through a tunnel at the entrance of the reservoir and conveyed in the river downstream the dam. A weir or a guide wall located at the upstream head of the reservoir re-directs the water to the tunnel during period of high flow and high sediments loads, and allows water entering the reservoir during period with low sediment loads. Alternatively, the intake structure can be located inside the reservoir, leading to some deposition in the upstream part of the reservoir.
An alternative to bypass sediments through a tunnel is in transporting them with trucks or boats. Accumulated sediments are excavated from the reservoir, bypassed around the reservoir via trucks or boats and transported downstream.
Methods, tools, and devices
During planning
The design of bypass tunnels depends on catchment characteristics like topography, geology, hydrology and reservoirs shape and size. (Tiger et al. 2011, Hauer et al. 2018). They function well in small reservoir with steep sides as the gradient of the diversion channel need to be sufficient to insure the transport of sediments. Bypass tunnels is a measure that do not interfere with hydropower operations since it does not require a drawdown of the reservoir. In addition, it induces less impacts on the downstream ecosystems than flushing or sluicing. However, bypass structures are not well adapted to flood control reservoirs as they undercut the main role of these reservoirs (Kondolf et al. 2014).
During implementation
Construction of bypass structures (canals or tunnels) have relatively high investments costs. They should be built at the time of reservoir construction to minimize technical efforts.
During operation
The main challenge of bypass tunnels is abrasion. Entrance of sediments degrades the inlets of the tunnels and can induce deep abrasion of the material. High strength concrete is recommended for the construction of the tunnels.
Relevant MTDs and test cases
| Relevant MTDs | |
|---|---|
| BASEMENT | |
| Bedload monitoring system | |
| HEC-RAS | |
| Shaft hydropower plant | |
| Relevant test cases | Applied in test case? |
| Gotein test case | - |
| Guma and Vadocondes test cases | - |
| Las Rives test case | - |
| Trois Villes test case | - |
Classification Table
| Classification | Selection |
|---|---|
| Fish species for the measure | Gravel spawners |
| Does the measure require loss of power production | Operational (requires flow release outside turbine) |
| - | |
| - | |
| Recurrence of maintenance | Irregular at events |
| Which life-stage of fish is measure aimed at | Spawning / Recruitment |
| Juveniles | |
| Adult fish | |
| Movements of migration of fish | |
| Which physical parameter is addressed | - |
| - | |
| - | |
| Substrate and hyporheic zone | |
| - | |
| - | |
| - | |
| - | |
| Hydropower type the measure is suitable for | Plant in dam |
| Plant with bypass section | |
| Dam height (m) the measure is suitable for | Higher than 10 |
| Section in the regulated system measure is designed for | - |
| - | |
| - | |
| Downstream outlet | |
| River type implemented | Steep gradient (up to 0.4 %) |
| - | |
| - | |
| Level of certainty in effect | Moderately certain |
| Technology readiness level | TRL 9: actual system proven in operational environment |
| Cost of solution | See cost table |