Difference between revisions of "Placement of spawning gravel in the river"
Bendikhansen (talk | contribs) |
Bendikhansen (talk | contribs) |
||
| (72 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[file:icon_habitat.png|right|150px|link=[[Habitat]]]] | ||
| + | [[file:icon_sediment.png|right|150px|link=[[Sediments]]]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note that this measure is included in both the habitat and sediment categories. | ||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
| − | [[file: | + | [[file:Eggs gravel.PNG|thumb|250px|Figure 1: Salmon eggs in gravel. The picture on the left shows high egg survival (transparent = alive) in placed spawning gravel. The picture on the right shows low survival rate in natural spawning gravel where sand has filled in much of the substrate]] |
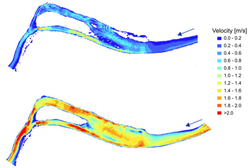
| − | + | [[file:spawning_gravel_model.png|thumb|250px|Figure 2: Example of simulation results from a hydrodynamic model. Flow velocity map for flow rate of 15.4 m<sup>3</sup>/s is shown at the top and for 100 m<sup>3</sup>/s at the bottom.]] | |
| − | The grain size | + | [[file:spawning_gravel_excavator.png|thumb|250px|Figure 3: Excavator placing spawning gravel in a river.]] |
| − | Before placement of spawning gravel in the river is made, the hydraulic conditions where the spawning gravel is placed must be investigated. The gravel must be located in a part of the river that does not dry out during low flow conditions, in areas with sufficient through-flow of fresh, oxygen-rich water to the eggs, and in areas that are not exposed to out-wash/flushing during high flow events. | + | |
| − | This measure has been implemented in | + | River regulations often change the natural flow regime and the sediment connectivity, introducing changes to the substrate composition both in the bypass section and downstream the outlet of the hydropower plant. This is often leading to a reduction in magnitude, frequency and duration of floods that impact the substrate composition, typically leading to fine materials clogging the substrate and possibly creating an armoured layer. An armoured layer will inhibit the spawning of fish species laying their eggs in the substrate, potentially reducing the number of eggs deposited in the substrate, increasing the predation and possibly also reducing the survival of eggs, e.g. due to low oxygen levels in the hyporheic zone. As such, the areas supporting spawning can be reduced due to regulation and hence represent a limiting factor ('bottleneck') for the fish population. |
| + | The grain size distribution of the spawning gravel to be placed in the river must be correct for the species of concern. The spawning fish should be able to dig and lay their egg in the added gravel. Fine sediments should not be able to clog the gravel. The shape of the stones should be similar to the natural conditions in the river, and sharp-edged stones from blasting, often available close to a hydropower projects, should only be used if considered appropriate for the species of concern. If the gravel is not sufficiently 'clean', it should be washed prior to deposition in the river to avoid particle pollution and possibly increased clogging downstream. | ||
| + | Before placement of spawning gravel in the river is made, the hydraulic conditions where the spawning gravel is placed must be investigated. The gravel must be located in a part of the river that does not dry out during low flow conditions, in areas with sufficient through-flow of fresh, oxygen-rich water to the eggs, and in areas that are not exposed to out-wash/flushing during high flow and flood events. | ||
| + | This measure has been implemented in several rivers in Norway (Pulg et al 2017). It is a fairly inexpensive measure to introduce, it stimulates the natural population and seems to achieve very good results in all rivers it has been used. | ||
=[[Methods, tools, and devices]]= | =[[Methods, tools, and devices]]= | ||
==During planning== | ==During planning== | ||
| − | A first step in considering placement of spawning gravel as a measure would be to assess if the total and distribution of spawning areas are limiting the development of fish population, i.e. diagnosis in the environmental design terminology. The spawning areas are often assessed by visual inspection of the river, i.e. by foot beside the river, by wading or from boat. Aerial photos can also in some cases assist this step. When the spawning areas are identified, they can be mapped in a GIS and the total area and their distribution assessed. For Atlantic salmon, spawning areas are considered being large if more than 10% of the total river has suitable spawning conditions, moderate if between 1-10% and small if less than 1% (Forseth | + | A first step in considering placement of spawning gravel as a measure would be to assess if the total and distribution of spawning areas are limiting the development of fish population, i.e. diagnosis in the environmental design terminology. The spawning areas are often assessed by visual inspection of the river, i.e. by foot beside the river, by wading or from boat. Aerial photos can also in some cases assist this step. When the spawning areas are identified, they can be mapped in a GIS and the total area and their distribution assessed. For Atlantic salmon, spawning areas are considered being large if more than 10% of the total river has suitable spawning conditions, moderate if between 1-10% and small if less than 1% (Forseth and Harby 2013). The distribution/spread is considered large if more than 500 meters between identified spawning areas, medium if between 200-500 meters, and small if less than 200 meters. These threshold values are considered indicative for Atlantic salmon, but they may be different for other fish species. |
<table style="height: 207px;" border="1" width="764"> | <table style="height: 207px;" border="1" width="764"> | ||
| + | <caption>Table 1: A system for an overall classification of spawning habitat for Atlantic salmon (Forseth and Harby 2013).</caption> | ||
<tr style="height: 13px;"> | <tr style="height: 13px;"> | ||
<td style="height: 13px; width: 264px;"> </td> | <td style="height: 13px; width: 264px;"> </td> | ||
| Line 55: | Line 63: | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| − | Hydraulic analysis can support the identification of the best location to place the spawning gravel, in order to meet the preferences of the fish of concern, avoid locations with too slow-flowing water and areas exposed to flushing during high flow conditions | + | Hydraulic analysis can support the identification of the best location to place the spawning gravel, in order to meet the preferences of the fish of concern. For typical gravel spawners, it is recommended to avoid locations with too slow-flowing water and areas exposed to flushing during high flow conditions. |
| − | |||
| − | [[ | + | A high number of hydro-dynamic and hydro-morphodynamic tools are available for such analysis with different functionality and data needs, ranging from more simplistic 1-dimensional (1D) hydraulic tools, to highly advanced 3-dimensional (3D) tools solving a range of partial differential equations (Navier-Stokes equations) in all directions. They all require detailed description of the bottom topography of the areas the gravel might be placed, and the flow regime the river will be subject to. As average flow velocities will not be sufficiently detailed to identify the best locations, 2D- or 3D models will be required. Examples of such models are [[River2D]], [[HEC-RAS|HEC-RAS 2D]], Flo-2D/[[FLOW-3D]], Mike21c, [[OpenFOAM]] and [[TELEMAC]] 2D and 3D. |
==During implementation== | ==During implementation== | ||
| − | The implementation of the measure would require access to substrate of suitable grain size distribution, shape and of proper mineral composition, preferably similar to the substrate naturally present in spawning areas. In order to transport and place the new material at the right locations in the river, heavy machinery such as dumpers and tractors would be needed. In case where the site is difficult to access, use of helicopters can be the best option. The dumping of the substrate in the river would normally require supervision of a biologist, | + | The implementation of the measure would require access to substrate of suitable grain size distribution, shape and of proper mineral composition, preferably similar to the substrate naturally present in spawning areas. In order to transport and place the new material at the right locations in the river, heavy machinery such as dumpers and tractors would be needed. In case where the site is difficult to access, use of helicopters can be the best option. The dumping of the substrate in the river would normally require supervision of a biologist, hydraulic engineer or another experienced person in order to secure the right positioning of the substrate, proper thickness of substrate layer and finish of the surface preparation. Hydro-morphodynamic models can also be used to guide the positioning. |
| + | The construction work will often require use of heavy machinery. Depending on the location of the river and how accessible it is and the costs, the transport of gravel will typically be made by dumper or by helicopter. If helicopter is used, the gravel can normally be dumped directly into the river, under the supervision of a biologist or another experienced person. If the new material is transported into the site by dumpers, an excavator will normally be needed at the site. This will also require the presence of an experienced person to ensure the correct placement and thickness of the gravel. | ||
| − | + | Habitat measures in regulated rivers must often be maintained unless the natural functions related to flow and sediments are restored, such as flood events and connectivity of the sediments. How often the maintenance must be made will differ from river to river and can vary from for instance every 5 year to every 20 years. Rivers with intense growth of moss, algae and macrophytes would need more frequent maintenance than rivers with cold water and low nutrient concentrations (less growth). | |
| − | + | ==During operation== | |
| − | + | Habitat measures in regulated rivers must often be maintained unless the natural functions related to flow and sediments are restored, such as flood events and connectivity of the sediments. How often the maintenance must be made will differ from river to river and can vary from for instance every 5 years to every 20 years. Rivers with intense growth of moss, algae and macrophytes would need more frequent maintenance than rivers with cold water and low nutrient concentrations (less growth). | |
| − | = | + | =Relevant MTDs and test cases= |
| − | + | {{Suitable MTDs for Placement of spawning gravel in the river}} | |
| − | |||
=Classification Table= | =Classification Table= | ||
| + | {{Placement of spawning gravel in the river}} | ||
| + | =Relevant Literature= | ||
| + | *Pulg, U., Barlaup, B.T., Skoglund, H., Velle, G., Gabrielsen, S.E., Stranzl, S.F., Espedal, E.O., Lehmann, G.B., Wiers, T., Skår, B., Normann, E., Fjeldstad, H-P. 2017. Tiltakshåndbok for bedre fysisk vannmiljø: God praksis ved miljøforbedrende tiltak i elver og bekker. Uni Research AS. | ||
| + | *Forseth, T., and Harby, A. 2014. Handbook for Environmental Design in Regulated Salmon Rivers. NINA Special Report 53. Trondheim: Norwegian Institute for Nature Research. | ||
| − | + | [[category:Habitat measures]][[category:Sediment measures]][[category:Solutions]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[category: | ||
Latest revision as of 11:45, 16 March 2021
Note that this measure is included in both the habitat and sediment categories.
Contents
Introduction
River regulations often change the natural flow regime and the sediment connectivity, introducing changes to the substrate composition both in the bypass section and downstream the outlet of the hydropower plant. This is often leading to a reduction in magnitude, frequency and duration of floods that impact the substrate composition, typically leading to fine materials clogging the substrate and possibly creating an armoured layer. An armoured layer will inhibit the spawning of fish species laying their eggs in the substrate, potentially reducing the number of eggs deposited in the substrate, increasing the predation and possibly also reducing the survival of eggs, e.g. due to low oxygen levels in the hyporheic zone. As such, the areas supporting spawning can be reduced due to regulation and hence represent a limiting factor ('bottleneck') for the fish population. The grain size distribution of the spawning gravel to be placed in the river must be correct for the species of concern. The spawning fish should be able to dig and lay their egg in the added gravel. Fine sediments should not be able to clog the gravel. The shape of the stones should be similar to the natural conditions in the river, and sharp-edged stones from blasting, often available close to a hydropower projects, should only be used if considered appropriate for the species of concern. If the gravel is not sufficiently 'clean', it should be washed prior to deposition in the river to avoid particle pollution and possibly increased clogging downstream. Before placement of spawning gravel in the river is made, the hydraulic conditions where the spawning gravel is placed must be investigated. The gravel must be located in a part of the river that does not dry out during low flow conditions, in areas with sufficient through-flow of fresh, oxygen-rich water to the eggs, and in areas that are not exposed to out-wash/flushing during high flow and flood events. This measure has been implemented in several rivers in Norway (Pulg et al 2017). It is a fairly inexpensive measure to introduce, it stimulates the natural population and seems to achieve very good results in all rivers it has been used.
Methods, tools, and devices
During planning
A first step in considering placement of spawning gravel as a measure would be to assess if the total and distribution of spawning areas are limiting the development of fish population, i.e. diagnosis in the environmental design terminology. The spawning areas are often assessed by visual inspection of the river, i.e. by foot beside the river, by wading or from boat. Aerial photos can also in some cases assist this step. When the spawning areas are identified, they can be mapped in a GIS and the total area and their distribution assessed. For Atlantic salmon, spawning areas are considered being large if more than 10% of the total river has suitable spawning conditions, moderate if between 1-10% and small if less than 1% (Forseth and Harby 2013). The distribution/spread is considered large if more than 500 meters between identified spawning areas, medium if between 200-500 meters, and small if less than 200 meters. These threshold values are considered indicative for Atlantic salmon, but they may be different for other fish species.
|
Extent of spawning habitat as a percentage of river area |
||||
|
Small (<1%) |
Moderate (1-10%) | Large (>10%) | ||
| Distance between spawning habitats (across all segments) |
Large (>500m) |
Small | Small | Moderate |
| Medium (200-500m) | Small | Moderate |
Large |
|
| Small (<200m) | Moderate | Large |
Large |
|
Hydraulic analysis can support the identification of the best location to place the spawning gravel, in order to meet the preferences of the fish of concern. For typical gravel spawners, it is recommended to avoid locations with too slow-flowing water and areas exposed to flushing during high flow conditions.
A high number of hydro-dynamic and hydro-morphodynamic tools are available for such analysis with different functionality and data needs, ranging from more simplistic 1-dimensional (1D) hydraulic tools, to highly advanced 3-dimensional (3D) tools solving a range of partial differential equations (Navier-Stokes equations) in all directions. They all require detailed description of the bottom topography of the areas the gravel might be placed, and the flow regime the river will be subject to. As average flow velocities will not be sufficiently detailed to identify the best locations, 2D- or 3D models will be required. Examples of such models are River2D, HEC-RAS 2D, Flo-2D/FLOW-3D, Mike21c, OpenFOAM and TELEMAC 2D and 3D.
During implementation
The implementation of the measure would require access to substrate of suitable grain size distribution, shape and of proper mineral composition, preferably similar to the substrate naturally present in spawning areas. In order to transport and place the new material at the right locations in the river, heavy machinery such as dumpers and tractors would be needed. In case where the site is difficult to access, use of helicopters can be the best option. The dumping of the substrate in the river would normally require supervision of a biologist, hydraulic engineer or another experienced person in order to secure the right positioning of the substrate, proper thickness of substrate layer and finish of the surface preparation. Hydro-morphodynamic models can also be used to guide the positioning. The construction work will often require use of heavy machinery. Depending on the location of the river and how accessible it is and the costs, the transport of gravel will typically be made by dumper or by helicopter. If helicopter is used, the gravel can normally be dumped directly into the river, under the supervision of a biologist or another experienced person. If the new material is transported into the site by dumpers, an excavator will normally be needed at the site. This will also require the presence of an experienced person to ensure the correct placement and thickness of the gravel.
Habitat measures in regulated rivers must often be maintained unless the natural functions related to flow and sediments are restored, such as flood events and connectivity of the sediments. How often the maintenance must be made will differ from river to river and can vary from for instance every 5 year to every 20 years. Rivers with intense growth of moss, algae and macrophytes would need more frequent maintenance than rivers with cold water and low nutrient concentrations (less growth).
During operation
Habitat measures in regulated rivers must often be maintained unless the natural functions related to flow and sediments are restored, such as flood events and connectivity of the sediments. How often the maintenance must be made will differ from river to river and can vary from for instance every 5 years to every 20 years. Rivers with intense growth of moss, algae and macrophytes would need more frequent maintenance than rivers with cold water and low nutrient concentrations (less growth).
Relevant MTDs and test cases
Classification Table
| Classification | Selection |
|---|---|
| Fish species for the measure | Gravel spawners |
| Does the measure require loss of power production | - |
| - | |
| Structural (requires no additional flow release) | |
| Recurrence of maintenance | Less often than yearly |
| Which life-stage of fish is measure aimed at | Spawning / Recruitment |
| - | |
| - | |
| - | |
| Which physical parameter is addressed | - |
| - | |
| - | |
| Substrate and hyporheic zone | |
| - | |
| - | |
| - | |
| - | |
| Hydropower type the measure is suitable for | Plant in dam |
| Plant with bypass section | |
| Dam height (m) the measure is suitable for | All |
| Section in the regulated system measure is designed for | - |
| Upstream of hydropower plant | |
| Bypass section | |
| Downstream outlet | |
| River type implemented | Steep gradient (up to 0.4 %) |
| Fairly steep with rocks, boulders (from 0.4 to 0.05 %) | |
| - | |
| Level of certainty in effect | Very certain |
| Technology readiness level | TRL 9: actual system proven in operational environment |
| Cost of solution | See cost table |
Relevant Literature
- Pulg, U., Barlaup, B.T., Skoglund, H., Velle, G., Gabrielsen, S.E., Stranzl, S.F., Espedal, E.O., Lehmann, G.B., Wiers, T., Skår, B., Normann, E., Fjeldstad, H-P. 2017. Tiltakshåndbok for bedre fysisk vannmiljø: God praksis ved miljøforbedrende tiltak i elver og bekker. Uni Research AS.
- Forseth, T., and Harby, A. 2014. Handbook for Environmental Design in Regulated Salmon Rivers. NINA Special Report 53. Trondheim: Norwegian Institute for Nature Research.